There have been some attempts to create a digital monetary system before, but all failed because an apparent problem called double spending.
The only bitcoin was able to survive thanks to being able to solve the “double spending” problem.
How was it possible and what the “double spending” problem actually is? Let’s get more in the depth of the thing.
What is „double spending“ and how it works?
In a nutshell, „double spending“ means spending the same money twice. Let’s explain it on a simple example from ordinary life. Imagine the following situation:
You go to a restaurant and order, let’s say, a lunch worth 20 USD. That 20 USD is now in cash vault of the restaurant. You simply cannot get the money back and spend the same money somewhere else to buy anything else.
The payment was made in cash i.e. with physical money, which is different than if you used bitcoin, i.e. digital currency. The fact that bitcoin is digital allows the transactions being copied and rebroadcasted. In theory, all this is a matter of copying one transaction in a computer and slightly modifying it. Simple, isn’t it? So there’s a possibility that the same bitcoin could be spent twice.
How is this even possible?
In that our example showed above, the payment was confirmed almost instantly because you paid in cash. But with digital currency it’s different. If the verification mechanism is missing it can lead to double spending. If there is not any mechanism for verification the payments, anyone can copy that digital money and pay at the same time somewhere else. Bitcoin solves the problem of being copied and getting spent twice efficiently. Let’s see why this solution is so unique.
A method used by bitcoin to handle the risk of double spending
How is bitcoin managing the double spending problem? Easy. By maintaining a universal ledger and implementing a confirmation mechanism. Simply called Blockchain. To learn more about blockchain see – What is blockchain and how does it work
About every 10 minutes, a block (i.e. a group of transactions) is added to the ledger (blockchain). So, the abovementioned blockchain technology prevents the double spending problem. Let’s see how the bitcoin network prevents the risk of double spending.
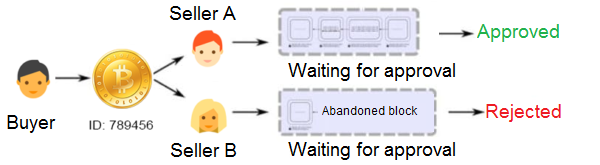
Imagine that you own 1 BTC (bitcoin) and want to spend it twice i.e. make two transactions simultaneously. You make transactions from your wallet to two other wallets. You assume that having 1 bitcoin in your wallet and executing the transactions simultaneously both transactions should go through, don’t you? Well, at first it does go through, but one of the transactions will be in-valid.
Verification of the right transaction is easy. Both transactions go into the pool of unconfirmed transactions. But only your first transaction will receive confirmation and will be verified by miners. The second transaction didn’t receive enough confirmations.
What happens in the case that both transactions are taken by the miners at the same time? In that case, the transaction that gets the maximum number of confirmations from the network will be included in the blockchain.
That’s why it is recommended to wait for (6 confirmations, every ten minutes one) so at all one hour. Before sending the goods paid by the customer in bitcoin. You can image confirmation as more blocks containing more transactions added to the blockchain, mathematically related to the previous one.
To be able to double spend that coin, the sender has to go back and reverse all transactions in the six blocks that have been added. It’s impossible to have the computing power to do this.
Potential double spending attacks:
51% attack If somehow an attacker captures 51% of the hash power of the network double spending can occur.
Hash power means the computational power which verifies transactions and blocks. If an attacker has this control he/she can reverse any transaction and make a private blockchain everyone will consider as real.
Because controlling 51% of the network is extremely expensive, no such attack has happened so far. The difficulty of the mining process, enormous costs of the hardware and the consumed electricity, all of which is infeasible to acquire.
So far, in the 10-year history of bitcoin, no such attack has been successful. The mechanism of a universal ledger (blockchain) based on confirmations has yet to be tricked.
Source of the information: CoinSutra.com