Hedging is a trading tool (or a strategy) widely used by large corporations, funds, but also by retail traders like yourself. How to use forex hedging in the form of securing a trade or forex strategies itself?
We’ll take a closer look at these topics in this article.
What is hedging?
What is hedging: Example
The word hedging does not hide any complexities, as it is simply a paired (opposite) trade. So, if you are in a long position with one tool (long = you have purchased), you eliminate it by the command sell (short = sale).
This may seem like nonsense at first glance, but there are situations in which hedging can be very useful. A typical example is securing an investment. If an open trade is no longer moving in the anticipated direction, making a hedge trade will ensure that your loss does not increase.
What is the significance of hedging?
To sum up, hedging can protect you against risk. For example, if you have a long (buy) position on EUR/USD 1 lot, but the market is not going in the needed direction, you can order sell 1 lot on EUR/USD and thus hedge the position. However, you should be careful, because hedging should already be a part of your forex trading strategy, or you should be more experienced traders, because you may secure the position for a short time, but at some point, the hedging must stop (by releasing one position or ending both).
Moreover, you need to be careful here. With Asian and European brokers, hedging is usually not a problem, but US brokers do not offer to hedge, and they will automatically close your last position with opposite trade. Always make sure your broker offers this option.
Possible realizations of hedging
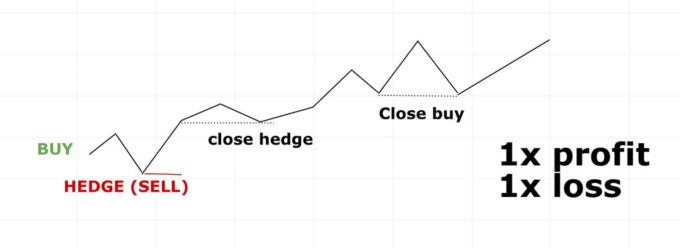
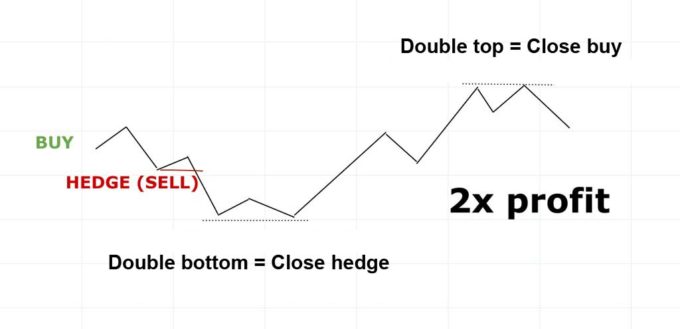
If you go for a hedge trade, you’ll basically face only 3 possible scenarios of how the trade can go. Either the price will still go against your original trade, or it will give you the opportunity to close the position gradually and end up with a profit. Look at the pictures below.
3 possible outcomes
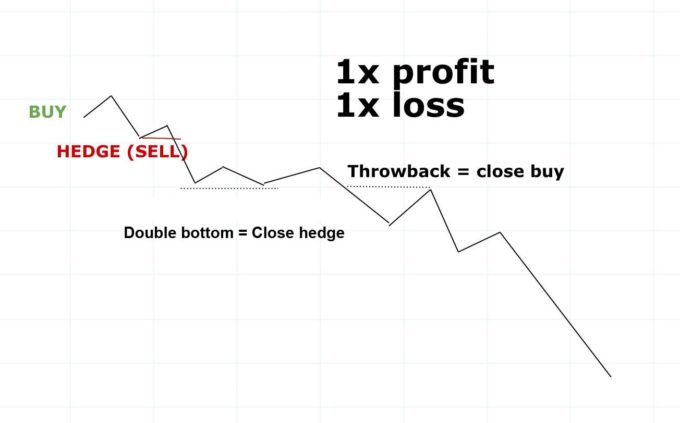
Hedging instead of stop-loss
Hedging can also be used instead of stop loss. If you reach the stop loss level, instead of closing the position, you enter the opposite position on the same or correlated pair to avoid further losses. If the price goes down, the loss on one of your positions will increase, but your hedging position will also increase profits.
Personally, I would use hedging mainly on shorter time zones (15M, 30M and so on). And when? You enter the position and the market will “flush” you out exactly on the stop loss, then it will return and give you a signal to enter the position from which it “flushed” you out. If you re-enter the same position again and risk the exact same stop loss being attacked, I would rather choose the opposite position instead of stop loss. But if the market turns aggressively, stop loss is the best choice. Hedging is only recommended for more experienced traders. The topic of hedging instead of stop-loss will certainly be dealt with in the following articles, the next question being the best places for leaving hedging. You already know from the pictures above that these may be for example double bottom or a top, but that is not the only option.
Correlated currency pairs
If you look at EUR/USD and GBP/USD or AUD/USD and NZD/USD, you will see that these instruments are positively correlated, i.e. moving in the same direction. By the way, this is useful to know even if you are no longer interested in hedging.
Why? Because if you enter a long (long) position at AUD/USD and at the same time enter NZD/USD, it is basically the same as if you were entering one position twice. When the US dollar falls, both pairs will be affected as well. Your risk is therefore so much higher, and it can disrupt your money management. Beware of correlated couples.
Demonstration of correlated pairs
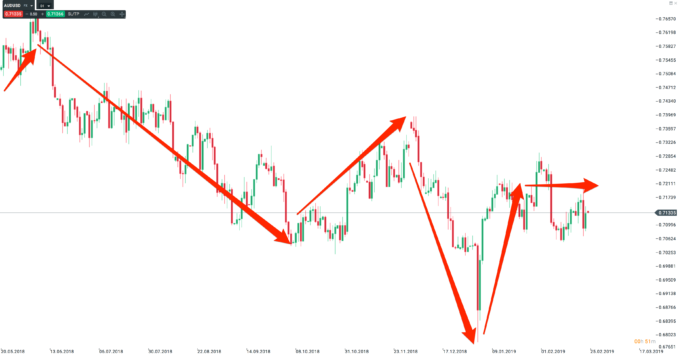
Hedging as a trading strategy
If you find correlated pairs, you can also use our help to determine where the potential is higher. For example, if you have a downtrend trading signal and you see close support on one pair, you will use the pair without support for trading and the pair with support for securing (usually in a smaller volume).
The hedging position is partly secured but still offers enough profit. Many forex brokers even support this strategy. Let’s be honest, the forex broker receives more money on fees (because you make two trades) and the customer (us) does a less risky trade, which is beneficial for both.
Other sources of information about hedging and money management:
- A good video explaining hedging insurance strategy: The Concept of Hedging (2018)
- Forex Money Management: Embracing losses leads to success
- Forex Money Management: Trading and psychology
- Forex Money Management: Martingale – An opportunity or a threat