It’s too complicated; isn’t it? Well, let ’s make it a little bit simpler.
In simple terms, blockchain is a kind of online ledger, a very specific kind of database. Unlike other databases, it is not centralized but decentralized which means that it has no central authority and is present on a large number of computers all over the world. The public blockchain is available to anyone. Writing data is only allowed based on a consensus of the financially engaged network participants – miners. It needs to be stressed that blockchain may not always be a public one. This system allows safe and permanent storing of transactions and data without a central governing authority.
The verification of the transactions is a job for the network. Network users participating in the validation (called miners) are rewarded for their effort in the form of network tokens (cryptocurrencies). Be it Bitcoin, Ethereum or Litecoin, they all can easily be exchanged for fiat currencies. Which is why their price is purely speculative.
Article content
- What is blockchain – simple explanation
- How does blockchain technology work?
- Blockchain and cryptocurrencies
- Smart contracts – Principle
- Risks and disadvantages
- Real examples of practical using of a blockchain
- Conclusion and recapitulation
What is so revolutionary about blockchain
- Safe – No mistakes made by humans, since there is no entity to control and influence it. Nobody is able to make changes retroactively.
- Decentralized– Blockchain doesn’t have any “center” and works thanks to its users on a peer-to-peer basis.
- Transparent– All transactions and activities within blockchain are transparent and can be easily traced back.
- All data is secured thanks to encryption using the hashing algorithm.
- Falsification of records in blockchain is extremely difficult (nearly impossible) activity
Blockchain = bitcoin? This equation is wrong, even though many people think so. The blockchain is a type of technology very much under the spotlight today, primarily due to bitcoin and the features it has. Why does it attract the attention of world powers and corporations? What makes this technology so revolutionary?
Since to understand the mechanics of blockchain in the entire complex is not easy, I assume that not everybody will be satisfied with the aforementioned simple and quick explanation. Having this in mind, on this page, I will explain blockchain technology in detail before we continue in more depth. What is blockchain, how does it work, what is it for and how can it change the world in the near future? These are the questions (and many more) that will be answered below.
What is blockchain? Technologically
Let’s start at a slow pace but a little bit more technically right from the beginning. The blockchain is a database. In IT, databases are used for storing data such as Instagram photos, video shots, e-shop products, and others. You can imagine a standard database as a large data center containing plenty of servers and hard-discs with flows of all sorts of information.
However, a database like this faces a fundamental problem: it is centralized (has central storage, warehouse). If you destroy, damage or switch off this data center you not only destroy the servers and hard-discs there but also all the data, which is a problem. With blockchain, this risk does not exist. The blockchain is not a standard centralized database. The blockchain is a distributed decentralized database (see an explanation of types of databases below). This means that you will not find it in one single place. You may say it is everywhere, it is indefinite and ever-lasting. You can imagine it as a never-ending ledger or Excel spreadsheet expanded by adding new records. Nobody can delete or turn off this “ledger”.
Blockchain has no central authority: No bank, government or institution – simply nobody (unlike the centralized database) – can control the blockchain. Nobody can destroy it, which is why people make so much fuss about this technology and why it attracts so much attention.
Nick Szabo (reported co-author of bitcoin) mentioned an analogy with amber. Why amber? He didn’t speak about any amber. What he had in mind was amber with a fly trapped inside millions of years ago. After all the years, the fly looks the same as it did in the prehistoric times. The fly has remained unchanged, not even time has left any mark. The fly is embedded in the amber like data in a blockchain.
As said above, no people, community or institution (or even time) can make a change, which is an undeniable advantage of this technology, making it so unique and attractive for people and the media. Bribery, data tempering and other infamous practices people are struggling with today may soon be relegated to history.
What is so revolutionary about blockchain? What is it for?
The blockchain is not such a new or young technology as many people think. All elements used by blockchain i.e. internet, cryptography and communication protocol are well known.
The technology itself is not such a revolutionary thing. It’s the methods used for interconnecting and using long-existing technologies.
Blockchain can be regarded as an evolutionary rather than a revolutionary technology. Today, there are many fields where blockchain technology can be used. Blockchain technology offers great potential for the future. Apart from allowing permanent data storage, what other areas can profit from this technology?
Blockchain technology may be applied in highly automated controlling of hierarchical processes in the security industry. As robots replace workers, blockchain is expected to replace clerks in the same way. A considerable part of investments made by various technological start-ups, world’s banks and multinational corporations is in blockchain technology. Part of our future, which may come sooner than expected, will have something to do with blockchain.
Everyone having technology as a hobby investing money in it sees blockchain as a tool that has the potential to improve efficiency and safety as well as to lay a brand new technological direction. If you are interested in concrete examples of using this technology take a look at specific areas of using blockchain.
Let’s take a closer look at the topic to help us better understand this exciting technology.
How does the technology work
We have already explained the basic information (what is blockchain, how it works). If you want to learn more in-depth first we must explore the term “database”, mention various types of databases, explain the process of confirming transactions and explore the double-spending problem. I’m sure you already have a few questions you want to ask. We will help you answer them. Let’s go ahead.
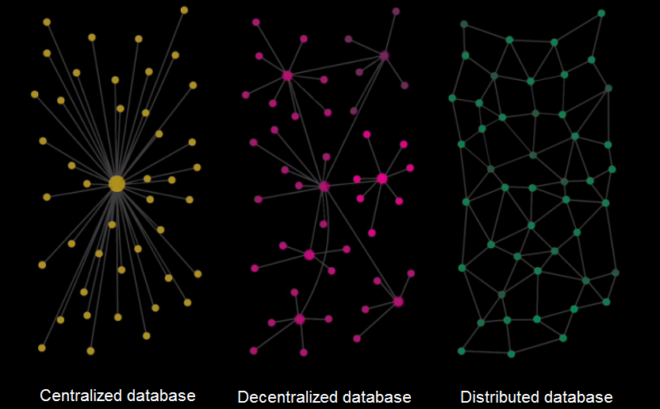
Centralized database – decentralized database – distributed database. What each term means and what principle is it based on? Let’s see and analyze them step by step.
Differences between basic types of databases
- Centralized database
We explained the term centralized database right at the beginning. It includes, for instance, saved Instagram photos and videos, e-shop products etc. This data can be found in a single centralized database, in a large physical data center containing a magnitude of servers and hard-discs. The problem of a centralized database rests in being centralized and, as such, vulnerable to destruction including all valuable data.
A huge disadvantage is a fact that a centralized database has one central authority making all decisions concerning the database.
- Decentralized database
Decentralization is closely related to distribution (functional on multiple devices). Decentralized database means that there is no central place or center so the data is not distributed from a single point but from more points – nodes. The data is distributed and the network modified by all network users based on defined rules. The advantage rests in being decentralized, so a failure of one user does not impact the rest of the network.
- Distributed database
Like 99 % other cryptocurrencies, bitcoin is running as a distributed database. A distributed database is an autonomous system taking care of itself. Nobody controls it; you won’t find any weak points there. It has no vulnerability to enable the attack. Its functioning does not require a huge data center to take care of the operation of the technology. The operation is carried out by all its users (which is why it is distributed) who are ordinary people mining coins on their computers, called miners. All data stored in the database is impenetrably encrypted by a hashing algorithm.
Are you interested in crypto mining? We have already written an article dedicated to this topic – Cryptocurrency Mining is Not What It Used To Be.
To get a better idea of the nature and functioning of the networks, there you can see an illustration of how it works in all types of databases:
It nicely shows what would be the impact of any potential attack on the centralized database. It’s enough to kill the main node and all data is gone forever. Another big disadvantage is the existence of a central authority, controlling the network. And, as you may suggest, there is no problem to tamper with the data.
All decisions about the decentralized database are reached jointly by all its users under pre-agreed conditions through consensus. So, blockchain is a decentralized database further distributed across the network through independent computers (i.e. “distributed” network).
Transactions and blocks: Key principles
Blockchain consists of two types of records: transactions and blocks. Transactions (e.g. conversion of cryptocurrencies) is data entered in the database by blockchain users reflecting actions carried out in a particular period. Each transaction is then collected and confirmed in blocks by miners. The confirmation process involves checking when and how each transaction was added to the database and whether the whole process complied with the rules. To put it in simple terms, while transactions are created by users, blocks are generated by miners on their computers.
Transactions created by users are smoothly transferred from one node to another depending on who is connected to whom at the given time. A valid bitcoin transaction is each transaction that:
- Contains a correct electronic signature of the user
- Indicates the visible transfer of money from the user’s wallet
- Meets other criteria such as a reward for miners or adequate time from recording the most recent transaction
Miners make an effort to create a block to confirm the transactions adding them to the blockchain and, connect them to another block to form a new block resulting in a “chain”(giving the name of the technology – BLOCK + CHAIN). Bitcoin miners are motivated by two things: The first one is the reward for mining a block and the second one is transaction fee attached by users to their transactions to get them processed by the miners. If you don’t attach the transaction fee your transaction will most likely not be processed. For more details see the article Confirming cryptocurrency transactions.
How are transactions confirmed?
The validation of transactions on a blockchain is a job for the network (in other words for the computers of the users). Users who participate in the validation through their voting are rewarded for their effort by network cryptocurrencies or tokens. Transactions can be confirmed by everybody but not everybody will be rewarded. Rewarded will be the first one to find the right solution, which can only be one miner. Needless to mention that rewards are distributed randomly. The more computing power your computer has, the more chances you have to crack the hashing puzzle to win a reward. Mining is a very computer-consuming process but the reward is worth it. (or better, was worth it. Now, competing against all the huge mining farms it’s no longer so lucrative).
The length of mining a block is for each crypto set separately. Mining of a bitcoin takes about 10 minutes. In theory, the more miners striving to find the right solution, the bigger the likelihood of finding such a solution sooner than within a 10-minute interval. This, however, never happens because the quantity of miners proportionally increases the complexity of the mining process so that it takes the defined 10 minutes.
Tokens (cryptocurrencies) gained from mining can be easily exchanged at specialized exchanges for fiat currencies (i.e. traditional currencies issued by governments such as USD, EUR, etc.).
Setting the real value of a cryptocurrency is somewhat problematic which means that the current price is more or less a speculative one.
The Bitcoin project is seen as the greatest financial experiment of the new era. The final total amount of tokens is known in advance (by 2140 almost 21 million tokens are planned to be mined ). This level will never be exceeded making bitcoin a deflationary asset in the long run.
Owing to its stability, simplicity, durability, and impossibility to falsify, in the future bitcoin will be used more and more, which applies to cryptocurrencies in general.
Blockchain and the double spending problem

Such non-planned copying – cryptocurrencies or digital items – may result in the collapse of the whole financial system, both real and gaming. The collapse of a gaming system has already happened in the virtual world. There is a danger this might happen in the real world, too.
At present, our traditional financial system prevents the occurrence of double spending due to the control by a central supervising authority, which will have stopped any attempted fraud. Obviously, this practice is far from being the most efficient solution.
Yet, no precautions are able to prevent the 51% attack. If somehow an attacker captures 51% of the hash power of the network, double spending can happen. If an attacker has this control he can “overtake” the existing branch. He/she can reverse any transaction and modify blockchain to invalidate all previous transactions. What the 51% attack does not enable is to create and sign transactions for accounts the attacker was denied to access.
There are many more safeguards for cryptocurrencies to diversify miner networks which means that such attacks can be effectively blocked. This type of attack is not a cheap one, it’s costly but also challenging. The attacker must make a big initial investment with a concrete cryptocurrency as well as be able to beat the computing power of the entire network. Even if he succeeds the network will be degraded by the attack resulting in the fall of the value of the crypto. At the end of the day, this attack will be absolutely counterproductive for the attacker. You can read more about the problem here at medium.com
How to prevent this blockchain problem? Do you want to learn more? Read our article on double spending problem giving you much more information.
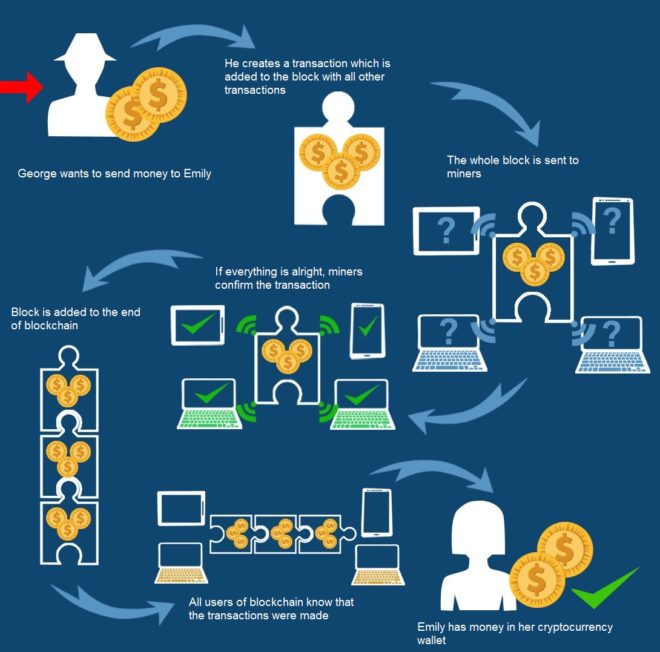
Infographic: Example of practical use of blockchain
People better understand an issue if it is illustrated in a picture or presented as a video. Having this in mind, we have prepared for you this simple info-graphics visualizing the payment process in the blockchain network. It shows a simple example: the transfer of money from point A to point B.
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies
I guess that the reason why you are interested in blockchain is not it’s huge future potential in data or identity protection. The reason why you heard about blockchain are most likely cryptocurrencies, the phenomenon of the present era.
There is no doubt that cryptocurrencies, namely Bitcoin, have made the technology popular worldwide.
To know what blockchain can be used for and how the technology works is always a useful thing. Many beginners believe that blockchain equals bitcoin, which is not true. We stressed it at the beginning. It’s also the reason for me believing that to understand the mechanism of a system you are going to invest in your money, no matter whether it is for buying or trading, is important. We have already given you some information. Now, we continue.
Why blockchain and cryptocurrencies
To combine bitcoin with blockchain technology was really a genius move. This technology allows cryptocurrencies to stay safe and decentralized.
Satoshi Nakamoto, one person or a group of people never revealing the identity, was behind the creation of bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency in the world using blockchain technology. Speaking of the relation between blockchain – including other cryptocurrencies – and bitcoin you can draw a parallel of the father (blockchain) and son (bitcoin). Right now, bitcoin is the world’s most valuable cryptocurrency with the biggest market capitalization. To learn more about bitcoin, read our bitcoin review.
Can you imagine seeing bitcoin work on a centralized database? Hypothetically, this would be possible but most likely nobody would want such a bitcoin and its value would be zero. If any government or institution such as police could freeze your coins or take them from your account the whole system would be for nothing.
Are you interested in cryptocurrencies but you don’t understand how come that such currencies have some real value given that they don’t exist and nobody can touch them? If these are the questions you would like to be answered don’t hesitate to read this article: How can I trust something that doesn’t even exist?
Smart contracts: What is it?
Similarly to the blockchain, smart contracts have gained popularity and increased attention recently. This is why we are going to talk about them a little bit more. As the name suggests, a smart contract is a kind of a smart or intelligent contract or agreement. How does such a smart contract look like? What issues does it address? Why you should know what a smart contract is?
The term “smart contract” was first used by Nick Szabo, an expert in computer science and cryptography, in 1977 – long before bitcoin was invented. His intention was to use distributed ledgers for storing contracts. Smart contracts are identical with normal (traditional) contracts with one difference: they are fully digital. A smart contract can be likened to a program stored in the blockchain.
How smart contracts work
Nick Szabo compares smart contracts to an ordinary vending machine. You insert a coin and the machine gives you a drink. If the machine identifies some problem with the coin it returns you the money. The machine is also able to return overpayments or cancel transactions. Everybody having enough coins can sign this ordinary contract.
The parallel between smart contracts and a vending machine does not provide the full picture. Using a vending machine doesn’t allow you to read the terms and conditions of the contract in advance, so you have to rely on the information received from the manufacturer of the machine. If things go wrong at the worst you may lose 1 USD. Getting no drink, having no money. Each loss is a loss, which is irritating, but the amount you lose by not getting your drink is negligible compared to losing all your property. Then, you will need something that is secure, credible and transparent, something like blockchain with asymmetric cryptography.
A real smart contract between two parties can be concluded by recording the contract into the Ethereum network (Ethereum is a cryptocurrency created in order to support Smart Contracts). This network guarantees that the contract will be performed under the rules derived from the contract’s source code available to anyone. Thanks to the blockchain, both parties can watch the progress of the contract.
Both parties, let’s say a buyer and a seller, deposit the amount of 1000 ether on the contract account, creating a guarantee of 2000 ether. If both parties confirm that the contract has been successfully completed (by seller sending the product and buyer receiving and paying for the product) both parties will be returned their deposited amounts. If the deal fails and one party attempts to cheat the other neither party will receive the guarantee. Hence, it is in the interest of both parties to make a fair deal.
Can bitcoin work on a smart contract
Naturally, it can. Nevertheless, it’s not very practical. Developers prefer other blockchains such as the aforementioned Ethereum, which fits best for this purpose. Using bitcoin protocol to conclude a smart contract is, however, possible. One of such users is particl.io – a blockchain eCommerce platform – using bitcoin protocol to manage its funds. The level of security it guarantees is lower than what’s offered by a more complex Ethereum platform.
Do all cryptocurrencies work on the blockchain
The vast majority of cryptocurrencies works on the blockchain. “Vast majority”, however, is not “all”. This technology is not used e.g. by IOTA or MaidSafe.
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain shaping the future? Or just a passing fad?
To answer the question of whether blockchain is a revolutionary technology or just a popular buzz word of these days is difficult to answer. One thing is certain. It is primarily bitcoin to have contributed to the boom catapulting cryptocurrencies and blockchain to historical levels.
You can’t deny all the huge benefits offered by blockchain demonstrated by the completed and running projects. Nevertheless, we still see some lack of understanding of what blockchain is or exaggerating the unexplored potential of this technology resulting in unrealistic ideas of its use.
Scores of large projects are already using this modern technology and hundreds of new ones are waiting in a queue. What if they extinct in a few years? What if their practical effect will be none or minimal? Who knows what will be the future of this technology, let’s say, 20 years ahead from now.
Blockchain: risks and disadvantages
All that we have said about blockchain so far have been superlatives. Each thing in this world seems perfect has a dark side. There is always some PRO and some CON. The blockchain is no exception. The blockchain is a technology like others. It can help you as well as it can turn against you.
For example, personal data. Personal data is something that can be abused easily. And what about data contained in a blockchain? Data that nobody will ever be able to erase!
Dictators and various oppressive regimes may use data from blockchain for strengthening their control over their citizens. They may curtail people’s liberties to a minimum. Having blockchain in their hands, it would be easy for all such regimes to unveil any attempted rebellion or coup or, to stage politically-motivated trials. On the contrary, a lot of activities would be more transparent which is not always desirable, either. In a nutshell, blockchain technology will provide good service to people unless it gets into the wrong hands.
Another disadvantage of blockchain is its excessive exploitation resulting in the slowdown of the network. Creating a block takes some time. Assuming that all people use the system simultaneously, the network is doomed to be overloaded. This is a temporary problem because of the effort to improve and modernize blockchain technology continues. If the overloading problem was not to be resolved it wouldn’t make sense to rollout blockchain technology on a global scale.
Also adding new records to the blockchain database requires enormous computing power, which logically increases power consumption. This increase is breathtaking. At various websites you can read how much energy running blockchain and adding new transactions to the bitcoin database consume; one of the studies says that it is a third of the Czech Republic’s annual production. Is it really that bad? Read this – Bitcoin mining is a waste of energy and harmful for ecology
Another obstacle for the deployment of blockchain technology is sufficient internet coverage, which is now in many countries of the world wishful thinking.
Specific areas of practical using of blockchain technology
Eventually, we have arrived at how blockchain technology can be practically applied in various fields and industries. While in some industries technology is already functioning even though we do not realize its presence, in other industries it will affect our lives in the future.
Take a look at six examples chosen by us demonstrating areas where blockchain technology could be used in the future (click on the box to display an example):
- Decentralized election – Thanks to the blockchain technology, democratic elections could finally be truly democratic. In the hands of the citizens.
- Land Registry – No one will be able to erase blockchain registration in the real estate cadastre and will be written there forever. This would effectively prevent unauthorized use of real estate, misappropriation of financial advances
- Finance – There are many things that blockchain can help in the financial sphere. For example, such financial audits can be done much more easily and efficiently. Instead of randomly checking transactions, each transaction can be checked using a specific code. It makes it easier to investigate frauds.
- Copyrights, intellectual property rights
- Transport of goods and origin of things
- Identity theft protection
- And many other examples…
The blockchain is more powerful than most people can imagine or admit. This is just a short list of examples of using blockchain. Here you can see that blockchain-based technologies already exist and work efficiently. Soon, we will see more and more coming…
Conclusion and recapitulation:

Sooner or later blockchain is going to affect our lives in the same way as the internet. Having this in mind, statements made by some professionals labeling blockchain as new internet may make more sense.
Thanks to its benefits and future prospects, blockchain is a phenomenon being adopted by the general public and various financial and technical organizations. We will see what the future will bring and how this technology takes root. Let’s make a short recapitulation of the main advantages of blockchain technology.
Main advantages of blockchain:
- The database is distributed among its users, making it safe and secure.
- The system works without being controlled by any central authority (which may undermine the purpose of the effort).
- Confirming of transactions is rewarded.
- The integrity of this type of database is protected by creating chains of blocks and the mining process.
- The authenticity of transactions is protected by asymmetric cryptography.
Finally, it’s not only blockchain technology that must be taken into account in our future projections. Cryptocurrencies too will play a major role. Yet, their quantity will shrink and the regulation will become more rigid than today. For example, the government of China already regulates all crypto-exchanges. Speaking of the future of cryptocurrencies, the number of questions is bigger than the answers. How many cryptocurrencies will survive? Will there be only one single crypto? Which one? Bitcoin? Nobody knows the answers. If you find crypto an exciting topic visit our comprehensive cryptocurrency section. It offers all kinds of information concerning cryptocurrencies for trading or buying.
It has been stressed on many occasions that we all should never stop learning. In the cryptocurrency business, this rule is relevant twice as much. Don’t live under the illusion that you know everything. There is always something new you may learn or grasp. Therefore, we have prepared several links to valuable info resources. You can read the texts or replay the videos.